What is a system boiler?

- What is a system boiler?
- System Boiler vs. Regular Boiler
- Key Distinctions Between System and Regular Boilers
- Regular Boilers: The Conventional Choice
- Complexity in Repairing Regular Boilers
- System Boilers: An Integrated Approach
- Maintenance and Installation Advantages of System Boilers
- Suitability Based on Home Size and Needs
- Economic Considerations of Boiler Types
- Making an Informed Decision on Heating Systems
- How Does a System Boiler Work?
- Advantages of System Boilers
- Simultaneous Use: A Key Advantage of System Boilers
- In-built Pressure System
- Seamless Transition in Upgrading
- Easier and Cost-effective Installation
- Efficiency and Maintenance Benefits
- Simpler Repairs with System Boilers
- Less Frequent and Cheaper Servicing
- Eco-friendly and Compatible with Renewable Technologies
- Cost Considerations
- Choosing the Right System Boiler
- Installation and Maintenance
- Energy Efficiency and Environmental Benefits
- System Boiler vs. Regular Boiler
Delving into the world of system boilers, it’s crucial to grasp what they are at their core. Commonly known as ‘sealed-system boilers,’ these devices are integral to providing both central heating and domestic hot water in your home. They achieve this through a sophisticated design that incorporates an inbuilt pump and an expansion vessel.
Unlike other heating solutions, system boilers stand out for their compact design and the integration of most essential components within the boiler itself. This design not only simplifies installation but also reduces the space needed for the setup. Think of it like a refrigerator, which operates independently without external parts – system boilers are similarly self-contained.
Understanding system boilers further, we encounter two key aspects: servicing and repair. Regular servicing is vital to ensure your boiler functions efficiently, especially during the crucial winter months. This includes a comprehensive check and cleaning of internal components to prevent issues caused by accumulated debris.
Awareness of potential faults is equally important to avoid expensive repairs. Warning signs like inconsistent heating, unusual noises, or a spike in energy bills indicate the need for a professional repair. When it comes to installation, the emphasis should be on correct connections and safety measures, such as installing pressure relief valves and thermostats.
By entrusting your system boiler’s care to skilled professionals, you ensure its longevity and optimal performance, making your home comfortable and energy-efficient.
System Boiler vs. Regular Boiler

Key Distinctions Between System and Regular Boilers
Understanding the differences between system and regular boilers is crucial for homeowners when considering their heating system options. Each type offers unique advantages and drawbacks, influenced by factors like home size and heating requirements.
Regular Boilers: The Conventional Choice
Regular boilers, also known as conventional boilers, have been a common feature in many homes. They operate on an open-vent heat only system, requiring a separate cold water storage tank and a hot water cylinder, often located in lofts or airing cupboards.
Complexity in Repairing Regular Boilers
Due to their multiple components, repairs for regular boilers can be more intricate. This complexity contrasts with the more unified design of system boilers.
System Boilers: An Integrated Approach
System boilers distinguish themselves by combining major components, such as the pump and expansion vessel, into one compact unit. This integration simplifies installation and maintenance, eliminating the need for separate tanks and cylinders.
Maintenance and Installation Advantages of System Boilers
The consolidated design of system boilers leads to more straightforward installations and less complicated maintenance routines compared to regular boilers. This aspect can simplify professional servicing tasks and annual inspections.
Suitability Based on Home Size and Needs
The choice between a system and a regular boiler depends on individual circumstances, such as the size of the property. Larger homes might benefit from regular boilers due to their capacity for delivering hot water simultaneously in different areas without affecting pressure levels.
Economic Considerations of Boiler Types
While regular boilers might incur higher maintenance costs due to their complex structure, system boilers offer a more compact and integrated setup. These structural differences have implications for both short-term and long-term costs, including installation, energy efficiency, and maintenance expenses.
Making an Informed Decision on Heating Systems
Recognizing the differences between system and regular boilers is key to an informed decision regarding home heating. This choice affects not only the initial cost but also long-term considerations like comfort, convenience, energy efficiency, and ongoing maintenance costs.
How Does a System Boiler Work?
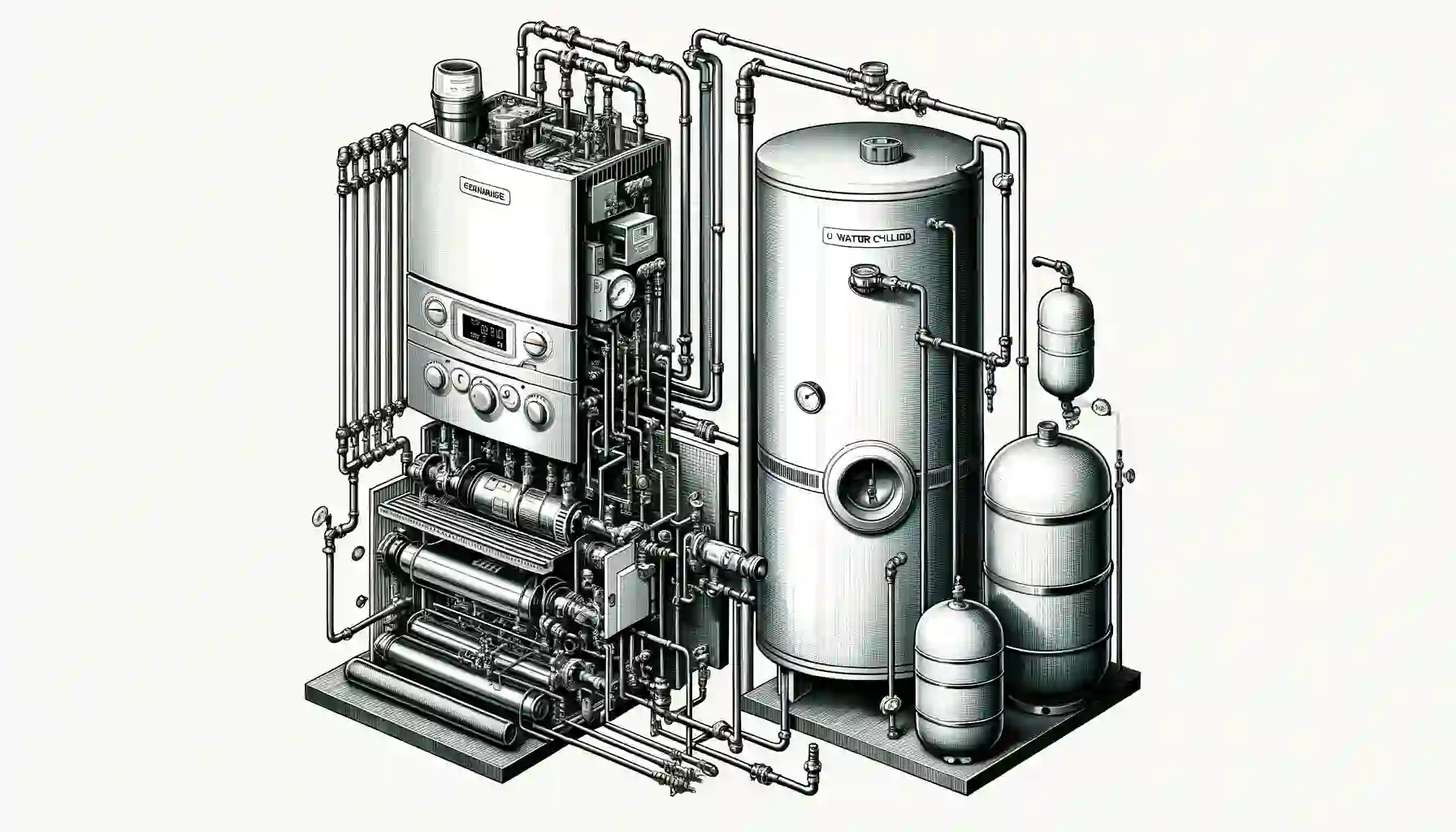
Understanding the Working Principle of a System Boiler
A system boiler, or ‘sealed system’, employs a simple yet efficient principle. It heats water within the boiler, which is then supplied to radiators and a hot water storage cylinder. This dual delivery ensures instant hot water access from your taps and showers.
Efficiency and Compactness of System Boilers
The design of system boilers is both efficient and compact, reducing the need for additional tanks or cylinders in your loft. Heating is initiated via your thermostat or directly from a tap, starting the process of water heating.
The Heating Process in System Boilers
Cold water enters the system boiler from the mains, heated by burners (gas or oil-fired). These burners are activated by an electric spark, and a heat exchanger transfers the heat to the water. This hot water then circulates through your home’s radiators, providing warmth.
Integral Components: Pump and Expansion Vessel
System boilers come equipped with an inbuilt pump and expansion vessel, negating the need for a cold-water feed tank in the loft. This is especially beneficial in homes where such installations are challenging due to space constraints.
Advantages of System Boilers

Simultaneous Use: A Key Advantage of System Boilers
System boilers are expertly designed to allow the use of hot water from multiple outlets simultaneously without a drop in pressure. This feature is especially beneficial for homes with multiple bathrooms or high hot water demand.
In-built Pressure System
Unlike combi-boilers, system boilers have an integrated pressure system, eliminating the need for a feed and expansion tank in the loft. This is particularly advantageous in homes where space is limited or loft access is restricted.
Seamless Transition in Upgrading
Upgrading to a system boiler from an older heating system is often smooth and cost-effective. Since they utilize components like hot water cylinders, the transition is less disruptive.
Easier and Cost-effective Installation
System boilers generally require fewer on-site components, leading to faster and less expensive installations compared to other boiler types.
Efficiency and Maintenance Benefits
With major components like pumps and expansion vessels built-in, system boilers are less prone to issues like airlocks or low pressure, making them more reliable and requiring less servicing over time.
Simpler Repairs with System Boilers
Repairs tend to be straightforward due to the integrated design of system boilers, often resulting in reduced repair times and costs.
Less Frequent and Cheaper Servicing
Servicing for system boilers is typically less frequent and more economical compared to other household boilers, thanks to their integrated design.
Eco-friendly and Compatible with Renewable Technologies
Modern system boilers boast high energy efficiency ratings, making them an environmentally friendly choice. They are also designed to work well with renewable technologies, like solar thermal systems, offering potential for additional energy savings.
Cost Considerations

Initial Investment in System Boilers
While system boiler installation generally incurs a higher upfront cost than regular boilers, it often becomes a cost-effective choice in the long term. The initial cost includes both the boiler and professional installation fees, which can vary based on job complexity and location.
Running Costs and Efficiency
System boilers are engineered for efficiency, leading to lower running costs over time. The integrated design, which often excludes a separate hot water cylinder, minimizes heat loss, thus reducing energy consumption and utility bills.
Aesthetic and Property Value Benefits
The compact and integrated components of system boilers not only save space but also offer an aesthetically pleasing appearance, potentially adding value to your property.
Importance of Regular Servicing
Regular servicing is crucial for maintaining optimum boiler efficiency and extending its lifespan, akin to an annual car tune-up. The cost of these services can vary depending on provider rates and any additional repairs needed.
Repair Costs for System Boilers
While repair needs are ideally minimal, if required, the cost will depend on the severity of the issue and whether it involves part replacements or adjustments. Regular servicing can often prevent these expensive repairs by addressing minor issues early.
Long-term Savings Potential
Despite the higher initial costs associated with purchasing and installing a system boiler, their high efficiency and reduced breakdown risks due to fewer external parts can lead to significant savings in operating costs and repairs over time.
Choosing the Right System Boiler

Assessing Household Needs and Property Size
When selecting a system boiler, consider your household’s hot water demand and the size of your property. Larger homes with multiple bathrooms need more powerful boilers than smaller residences.
Compatibility with Existing Heating Systems
If transitioning from a regular to a system boiler, additional space may be required for the expansion vessel and pump. Assessing the compatibility of the new system with your existing infrastructure is crucial.
Balancing Boiler Capacity with Usage Frequency
Choose a boiler that matches your usage patterns. Smaller households with less frequent hot water needs might benefit from lower-range models, while larger homes or commercial settings with higher demand should consider higher-capacity boilers.
Future Servicing and Repair Considerations
Opt for brands known for reliability and excellent after-sales service. A robust warranty can ensure future issues are handled efficiently by experienced technicians.
Professional Consultation for Optimal Choice
Consult with professionals to evaluate your property’s size, the number of occupants, and optimal installation locations. This includes considering access for maintenance and repairs.
Cost and Feature Considerations
Higher-end system boiler models may offer advanced features like programmable timers or energy-saving functions, potentially offsetting the initial investment through reduced operational costs. However, cheaper models might lead to higher maintenance expenses or more frequent repairs. Weighing the pros and cons is essential for an informed decision.
Installation and Maintenance

Understanding the Installation Process
System boiler installation is a complex process that requires professional handling. Due to the integration of many components, it’s less straightforward than installing other boiler types.
Importance of Professional Installation
Engaging an experienced and certified engineer is vital for optimal and safe operation of the system boiler. They can also advise on the most efficient boiler location, considering maintenance accessibility and gas supply proximity.
Regular Servicing for Efficiency and Longevity
Post-installation, regular servicing is essential to maintain your system boiler’s efficiency and extend its lifespan. Servicing tasks include checking all parts’ functionality, monitoring pressure levels, cleaning key components, and inspecting for wear and tear.
Preventive Maintenance Checks
Regular checks on crucial components like heat exchangers and valves are necessary to prevent deterioration. Monthly inspections can be useful for spotting potential leaks, blockages, or issues with water levels.
Handling Repairs with Expertise
System boiler repair might be required for issues ranging from simple part replacements to more extensive repairs. Due to the complexity of these systems, it’s recommended that repairs are conducted by qualified professional engineers with specific knowledge of system boilers.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Benefits

High Energy Efficiency of System Boilers
System boilers are highly energy-efficient, a key factor in their popularity. They effectively convert fuel into heat, minimizing wastage, which aids in reducing heating costs and carbon emissions.
Optimal Fuel Utilization
The energy efficiency of a system boiler ensures that a larger proportion of the fuel is used for heating water and the home, rather than being lost through inefficient processes.
Professional Installation for Maximum Efficiency
Accredited professionals should always undertake system boiler installation to ensure optimal setup for peak energy efficiency. Proper installation can enable system boilers to achieve over 90% energy efficiency.
Environmental Impact and CO2 Emission Reduction
System boilers contribute to mitigating climate change effects by significantly reducing CO2 emissions. Choosing an energy-efficient system boiler is a practical way homeowners can help reduce their carbon footprint.
Maintenance for Sustained Efficiency
Regular servicing of a system boiler maintains its high energy efficiency and helps in early detection of potential issues, contributing to long-term environmental benefits.
Inherent Reliability and Infrequent Repairs
While occasional repairs might be necessary, the inherent reliability of well-maintained system boilers means fewer repair needs, further cementing their eco-friendly status.
Eco-friendly Disposal
The recyclability of system boiler components exemplifies their support for eco-friendly practices. From installation and operation to disposal, a high-efficiency system boiler aligns with environmental conservation efforts.
In Summary
System boilers emerge as a superior choice for modern homes, especially suited for larger properties or those with high hot water demands. Their design, which integrates essential components, simplifies installation and maintenance while enhancing energy efficiency. This efficiency not only leads to long-term cost savings but also aligns with environmental goals by reducing carbon emissions. Choosing the right system boiler involves considering factors like home size and hot water requirements. Regular servicing by qualified professionals is crucial to maintain optimal performance. Despite a higher initial installation cost compared to regular boilers, the operational efficiency and lower maintenance needs of system boilers make them a cost-effective and eco-friendly solution for home heating.
